Help
1 Data
1.1 Peptide Information
| - | Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| General information | DRACP ID | The field provides the unique accessing number linking to the corresponding DRACP entry. |
| Peptide Name | Name of each peptide in DRACP. | |
| Sequence | The peptide sequence which is represented by single letter codes. L-amino acids are expressed in capital letters, and D-amino acids are expressed in small letters. X refers to modified amino acids. | |
| Sequence Length | Number of resiudes in the peptide sequence. | |
| Uniprot ID | Provide the accessing link(s) directing to external Uniprot entry(or entries). | |
| Source | The organism where the peptides or proteins were extracted or isolated. | |
| Type | Peptides are divided into Native peptide and Synthetic peptide according to their origin. | |
| Classification | Classificed by peptide type or mechanism. Including Molecularly targeted peptides, Cell-penetrating peptides, Tumor-homing peptides, Membrane-targeted mechanism, Apoptosis mechanism, Antiangiogenic mechanism... | |
| Activity information | Anticancer activity | Anticancer or antitumor activity verified by experiment. Including Cell Line, Disease, Cancer Classified, Activity, Testing Assay and Time. Data from literature or patents. |
| Hemolytic Activity | Hemolytic activity information against red blood cells (RBCs). | |
| Normal (non-cancerous) Cytotoxicity | Cytotoxicity information against normal (non-cancerous) cell line. | |
| Target | The action site of peptides against cancer cell. | |
| Affinity | Binding affinity between peptides and targets. | |
| Mechanism | The mechanism of peptides acting as anticancer agents. | |
| Nature | Biological activity classification. Except anticancer, it also includes Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antiviral... | |
| Structure information | PDB ID | Provide accessing link(s) directing to the correspong PDB entry. |
| Predicted Structure | Structure predicted by Alphafold, Show with Mol*viewer, click can download the PDB files. | |
| Helicity | α-helix percentage | |
| Linear/Cyclic | Linear or cyclic of peptides | |
| Disulfide/Other Bond | Disulfide bond (DSB) or other bond, such as sidechain-mainchain bond (SMB), N-C termini peptide bond (NCB). | |
| N/C-terminal Modification | The modifications of N/C-terminal according to the references | |
| Other Modification | Special amino acids (out of 20 common amino acids). | |
| Chiral | The L/D amino acids consist peptides. | |
| Physicochemical Information | Formula, mass, pI, Net charge and other information. | |
| Literature Information | The information of peptides come from all kinds of literature or patents, and the section provides the way to find the full text. | |
| Link | Link to other peptide databases. | |
1.2 Peptide Drug Information
| - | Fields | Description |
|---|---|---|
| General information | DRACPC ID | The field provides the unique accessing number linking to the corresponding DRACPC entry. |
| Active Ingredients | Active pharmaceutical ingredient. Substance in which the drug actually works. | |
| Description | Drug description. | |
| Synonyms | Other names of drug. | |
| Type | Drug type, mainly including small molecule drug and biotech drug. | |
| Disease | Applicable diseases. | |
| Classification | Drug Categories. | |
| Structure information | Molecular Formula, Molecular Weight, Active Sequence, Sequence Length, Modification and other structure information. | |
| External Codes | External identification code, also provides the accessing link to PubChem, DrugBank, NCI Thesaurus and GSRS. | |
| Drug approval | Including drug approval and clinical information. | |
2 Search help
2.1 Quick Search (Home page and Navigation bar)
Quick search allows keywords searches for sequence, peptide name and DRACP ID fields in the whole DRACP, including Peptide Library and Drug Library:
- Identify the keywords of interest for your search.
- Enter the terms (or key concepts) in the search box.
- "Enter".
2.2 Simple Search
The Simple Search page allows you to search individual fields in Peptide Library.
- Find a list of all indexed fields in the drop down menu and choose one of your interested.
- Enter the appropriate contents in the text area below.
- Click "Submit" (or click "Reset" to clear your input).
- Sequence >>> Single letter code (no space, mature peptide only) .e.g.FLPLLAGLAANFLPTIICKISYKC
- Peptide Name >>> Name of peptides (full name or short name works) .e.g.Buforin IIb or Buforin
- Sequence length >>> Enter the peptide sequence length number. e.g.21
- Origin >>> Origin of peptides (full name or short name works). e.g.Skin secretions of Rana rugosa or Rana rugosa
- UniProt ID >>> Accessing number and linking to UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot entries. e.g.P80400
- PDB ID >>> Accessing numble of Protein Data Bank. e.g.1JMN
- Linear/Cyclic >>> Structural properties of peptides, linear or cyclic. e.g.linear
- Chiral>>> Stereochemical properties of amino acids. e.g.L
- Cell Line >>> Cancer cell lines used for activity determination. e.g.K562
- Pantent ID>>> Anticancer peptide patent query, enter the patent number. e.g.US2018/0057532A1
- Pubmed ID>>> Anticancer peptide literature query, enter the Pubmed ID. e.g.14499271
- Nature >>> By other Natrue searches for anticancer peptide. e.g.Antimicrobial
2.3 Advanced Search
Through any combination of keywords input panel retrieval. The relationship between each item is "and".
2.4 Drug search
The Drug search page allows you to search individual fields in Drug Library.
- Find a list of all indexed fields in the drop down menu and choose one of your interested.
- Enter the appropriate contents in the text area below.
- Click "Submit" (or click "Reset" to clear your input).
- Active Sequence >>> Single letter code. e.g. AGCKNFFWKTFTSC
- Sequence length >>> Enter the peptide sequence length number. e.g. 10
- Active Ingredients >>> Name of active ingredient of the ACP drug. e.g. Triptorelin
- PubChem CID >>> PubChem identification code. e.g. 25074470
- DrugBank Accession Number >>> DrugBank identification code. e.g. DB06825
- UNII >>> UNII identification code. e.g. 9081Y98W2V
- CAS >>> CAS identification code. e.g. 57773-63-4
3 BLAST help
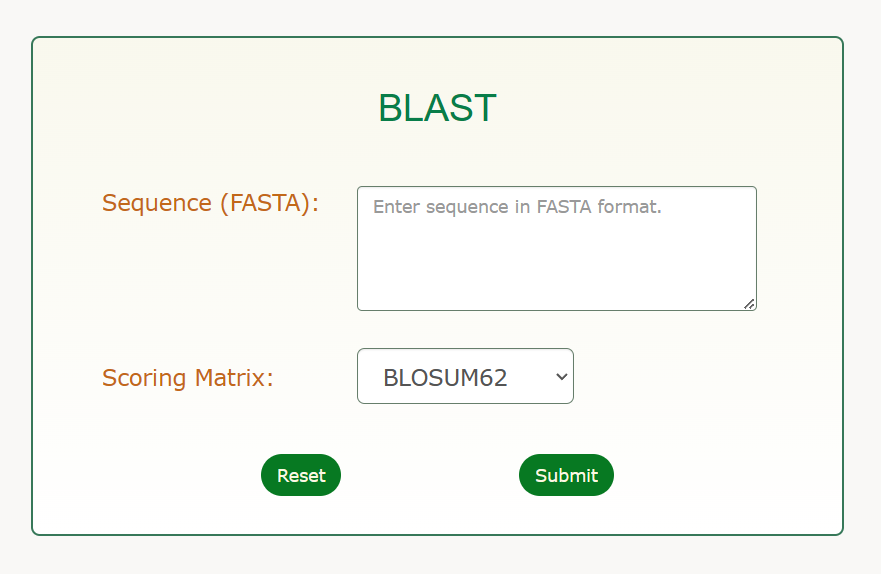
The BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) program uses a strategy based on matching sequence fragments by employing a powerful statistical model to find the best local alignments (For more information see http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/sss/ncbiblast/).
Usage Introduction
Step 1 – Sequence Input
- Sequence Input Window: The query sequence can be entered directly into text area. The sequence must be FASTA format.
FASTA format: FASTA formatted sequence records start with a definition line, which must start with a > character. The definition line must occupy one single line and followed by sequence data.
Example:
>
FLPLLAGLAANFLPTIICKISYKC
Step 2 – Parameters
- Matrix: This option allows you to choose the scoring matrix to be applied to the search.
Default value is: BLOSUM62
Tip: In general, higher value BLOSUM matrices (e.g. BLOSUM90) and lower value PAM matrices (e.g. PAM30) are more stringent than low value BLOSUM or high value PAM matrices. This implies that if you want to find more distantly related homologues, you should preferentially employ a low value BLOSUM or high value PAM matrix (For more information about scoring matrices see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Matrix).